- Ssh -L 5901:myUser@computer.myHost.edu:5901. I use it to do VNC over SSH. How do I convert that command into something that will work in a /.ssh/config file? Ex: host yam HostName yam.myHost.edu User myUserName all I want to do is type: ssh yam And have it open a SSH shell with a local listen port, and a remote port forwarded to it.
- Make SSH easy by adding entries to your local SSH config file. From this file we can set useful defaults to make logging into remote servers as easy as `ssh myserver`.
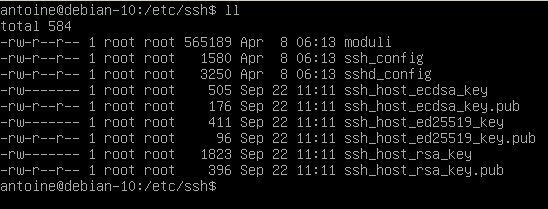
Sshdconfig is the OpenSSH server configuration file. How to configure and troubleshoot. Avoid getting accidentally locked out of remote server.
Configure how SSH runs on the server for better security.
We'll log into a server and edit the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file, to change how users can use SSH to log into the server from remote locations.We previously have used our local ~/.ssh/config file to easily log into a server. Let's now see some SSH options on the remote server, to see how we can affect who can log in and how.
SSH configuration is generally found in /etc/ssh/sshd_config.
Change SSH Port
We can change the port users use to login away from port 22.
Change the Port option to something other than 22:
Then restart SSH:
We can then try to login from our local computer by adjusting the port to use:
I usually keep port on standard port 22 and use other security means to lock this down.
Create New Admin User
We don't want user root to be able to login over SSH, as that user has no limits in privileges.
Creating a new user, who can use 'sudo', but isn't the root user, adds security:
- SSH key usually provides a first (separate) password needed, so attackers need both the SSH private key and knowledge of this password
- User then required to use their own password on top of that to run privileged commands via 'sudo'. This is missing when logged in as 'root' directly.
- We remove a vector of remote attack - root user cannot be logged into remotely
On the remote server, logged in as user root, we create a new user fideloper:
Then add user fideloper to group sudo, which allows that user to use 'sudo' commands:
Log in as user 'fideloper'

Next we want to make sure we can log into user 'fideloper'. To do so, we get our previously created id_sshex.pub (on our local computer) and paste it into the authorized_keys file of the new 'fideloper' user on the remote server.
Then, once again locally, edit the ~/.ssh/config file to adjust user from 'root' to 'fideloper':
Make it look like this:
Save that and then attempt to log into our server (again, from our local computer):
And we should get logged in as user 'fideloper'!
Disable SSH login of user root
Back on the remote server, let's edit the sshd_config file some more and lock down who can login and how further.
Disable the login of user root:
Save that and restart SSH:
Back on our local computer, try to login as root again:
This will ask for a password but tell is permission is denied, even if using the right password.
Disable password authentication
On the remote server, edit sshd_config and turn off the ability to login over SSH using password:
Edit the 'PasswordAuthentication' directive:
Save that and restart SSH:
Locally, try to login as user 'root' again and see you get permission denied: Clash of magic game apk download.
Allow SSH login by user or group
On the remote server, edit sshd_config and explicitly set which users can SSH into the server:
Add the 'AllowUsers' directive:
Save that and restart SSH:
Locally, log in as user 'fideloper' successfully:
Back on the remote server, let's use the 'AllowGroups' directive instead:
Add the 'AllowUsers' directive:
2013 mathrubhumi calendar pdf. Save that and restart SSH:
Locally, add a new Terminal tab (DON'T LOG OUT OF YOUR CURRENT SESSION) and try to login again:
You'll get denied, as none of our users are in group 'allowssh'.
On the remote server, create that group and assign it to user 'fideloper':
Locally, try to login again and see that you can login:
In the end, I allow both 'allowssh' and 'sudo' group to login over SSH:
As always, save that and restart SSH:
Short and complete guide to configure SSH on Cisco router and switch for secure remote connection. The Secure Shell (SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. The best-known example application is for remote login to computer systems by users.
SSH provides a secure channel over an unsecured network in a client-server architecture, connecting an SSH client application with an SSH server. Common applications include remote command-line login and remote command execution, but any network service can be secured with SSH. The protocol specification distinguishes between two major versions, referred to as SSH-1 and SSH-2.
The typical use of SSH Protocol
Local User Ssh Config
The protocol is used in corporate networks for:
- providing secure access for users and automated processes
- interactive and automated file transfers
- issuing remote commands
- managing network infrastructure and other mission-critical system components.
Configure SSH on Cisco Router or Switch
To configure SSH on Cisco router, you need to do:
- Enable SSH on Cisco router.
- Set Password for SSH.
- Force remote access to use SSH.
- Enable Password Encryption.
- Add domain name Server (DNS).
- Add Username and Password.
Let’s enable and configure SSH on Cisco router or switch using the below packet tracer lab. The configure on a packet tracer lab and real Cisco devices are the same. Just try to learn and do it what the SSH remote authentication needs.

Download the packet tracer lab or create your own lab. SSH Configuration Packet Tracer Lab.
In this example, I just enable and configure SSH on SW1 and trying to access it from PC1. It’s enough to learn how to configure SSH on Cisco router.
That’s all. Let’s check the process one by one.
- I have set DNS domain name with “IP domain-name” command.
- Then configure the router to use RSA key pair with modulus size of 1024 bites for remote service authentication with “crypto key generate rsa” command.
- Add username “Admin” with Password of “Technig” for ssh authentication.
- Enabled ssh with “line vty 0 4” command.
- Configure ssh to use local username and password with “login local” command. Remember that you can set a username and password for ssh with “username Admin password Technig” command as well. But here we configure ssh to use local username and password.
- Configure the router to accept only ssh connection with “transport input ssh” command.
- Configure ssh to version 2 using “IP ssh version 2” and set the authentication times to 3 with “IP ssh authentication-retries 3” command.
- Finally set the ssh timeout to 120 seconds with “IP ssh time-out 120” command.
Ssh Config Addkeystoagent
Related Article:Install SSH on CentOS 8.x and Red Hat Linux
The final step is to test the connectivity of ssh from PC1 with “ssh -l Admin 192.168.1.1” command for command prompt.
Linux Local Ssh Config
OK, the ssh works perfectly.
